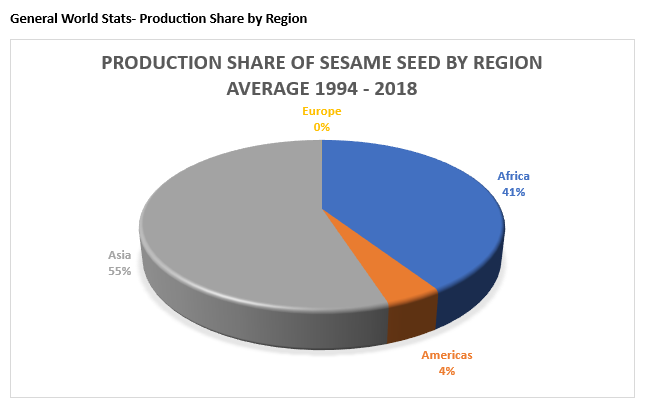
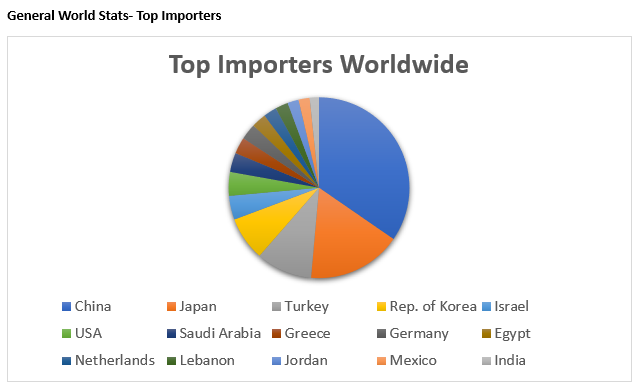
Sesame in the World: a brief introduction and statistics
classified as a health food in Asian countries. Sesame seeds contain significant amounts of oil, proteins, carbohydrates, essential minerals, large amounts of methionine and tryptophan, fiber, and secondary metabolites such as lignans, saponins, flavonoids and phenolic compounds. In addition, the seeds are a good source of calcium, phosphorus and iron and are rich in B vitamins, E and a small amount of trace elements. Sesame consumption in the world is constantly increasing, mainly due to the changing consumption habits of consumers and increasing health awareness. Today, consumers mostly prefer products with high nutritional value. Therefore, the demand for sesame seeds is higher as they have several nutritional properties such as vitamins, minerals, fibers, healthy fats and proteins. About 70% of the world's sesame seeds are used to make oil and flour. The total annual consumption of oil and food is approximately 65% and 35% respectively.